
10.2 Configuration of remote hosts
This dialog box allows to configure the remote hosts that can be used to run calculation jobs. In this way, it's possible to use the power of other systems connected trough TCP/IP protocol (e.g. PCs, workstations, HPC systems), reducing the computational time.
10.2.1 The calculation host concept
The calculation host is a logical unit used by VEGA ZZ to perform a
calculation. There is no difference if the unit is placed in a local or in a remote machine,
because the software layer selects automatically the more appropriate
communication protocol. The advantage of this
implementation is the totally transparency at the user side, allowing to run
local or remote jobs in the same easy way.
The most common scenario in computational chemistry research laboratories, is
the installation of a reduced number of high performance calculation systems (HPC)
and a large number of middle-low performance PCs. These PCs can dramatically
increase their computational power submitting the calculations to HPC
systems in transparent and interactive way. The first implementation of this
technology is available for AMMP: a molecular mechanics software integrated in
the VEGA ZZ enviroment.
VEGA ZZ is able to manage three host types: local host, master host
and child host. The local host is automatically configured when the
software starts and it can be used to perform local calculations. In this case
the computational power depends on the hardware running VEGA ZZ.

VEGA ZZ uses the pipe protocol to communicate with AMMP
which is the application example managed by the host. The piping process is
implemented in the operating system and it consists to put the output of a
program as input of another one and vice versa. It is much faster then
the TCP/IP connection used for the remote hosts (see below).
Each physical remote host is called master host from which is
generated one or more child host. It is a virtual host corresponding to each
manageable thread, one for each physical CPU installed in the remote system. As
an example, if a master host has installed two CPUs, it can manage two
calculation threads at the same time and so it are generated two child hosts
capable to run two single-threaded application at the same time.
The communication with the remote hosts is implemented by TCP/IP and it's based
on the telnet protocol. For this reason, the remote host must have a full
configured telnet service.

In the Windows hosts, it's strongly recommended to use the WarpTel service instead of the Microsoft's telnet service for security reasons (see below).

The telnet protocol is insecure because all TCP/IP packets are sent in clear form. For this reason, it's strongly recommended to use the encrypted connection, available in the WarpTel service:
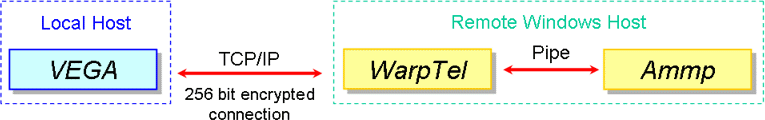
The TCP/IP packets are sent on the net
using a 256 bit encryption and are encoded/decoded on-the fly by VEGA ZZ and
the WarpTel service.
The telnet daemons available in the Unix systems don't have the capability to
encode/decode the packets and so you must use the
WarpGate service to create a secure
encrypted connection.
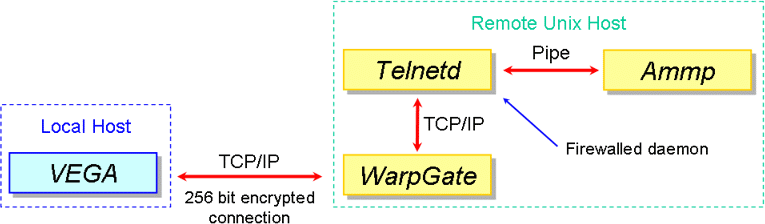
The telnet daemon must be protected by a firewall, otherwise the system could undergo to malicious attacks. To install the WarpTel and the WarpGate services, consult their documentation.
10.2.2 Host configuration
The dialog is accessible selecting Tools
![]() Host configuration in the
main menu.
Host configuration in the
main menu.
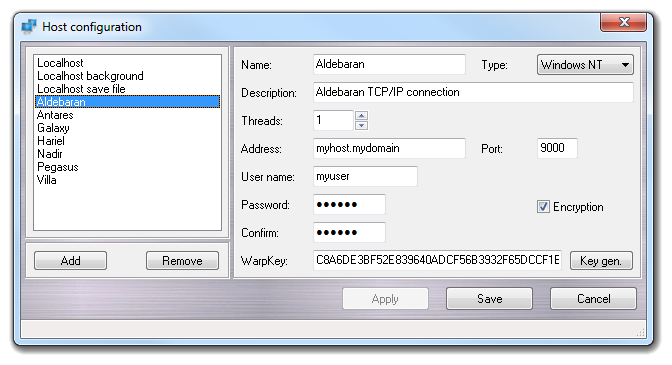
In the right corner is located the master
host list. The child hosts aren't not visualized in this
window because they have the same configuration parameters of their master host.
The child hosts are shown in the calculation dialogs such as in the AMMP's one.
The first three hosts in the list are called local hosts and they can't
the changed with this window, because they are automatically configured when
VEGA ZZ. They can be used to perform calculation using the local hardware
(default condition) and in this case the faster pipe communication is used
instead of the TCP/IP protocol. Selecting Localhost in the application
control panel (e.g. AMMP calculation window), the calculation is immediately
executed in interactive mode (if you close VEGA ZZ, the job is stopped);
selecting Localhost background, the calculation is started in background
and it can't be controlled by VEGA ZZ (if you close VEGA ZZ, the job continues
without stopping itself); selecting Localhost save file, the calculation
is not started and the input file is created to run the job later.
Add and Remove buttons, respectively, creates a new host and
removes the selected host. In the right box, it's possible to change the host
Name, the Description and the Type (Unknown, Unix, Linux,
Windows 9x, Windows NT). Please pay attention selecting the host type, because
a wrong selection make the connection unusable: use Unknown if you don't
know the remote host operating system, Unix or Linux for *nix operating systems,
Windows 9x for the old Windows operating systems (Windows 95, 98 and ME) with
the WarpTel standard version, Windows NT for Windows NT, 2000, XP and Vista with
the WarpTel standard or service version.
The number of the childs for each master host is controlled by the Threads
filed, which values must be in the 1 to 65535 range. It correspond to the number
of the installed CPUs or CPU cores: dual core CPUs are as two physically
separated CPUs and each one is equivalent to two normal CPUs (e.g. 2 x dual core
CPUs = 4 threads). The CPUs with the Hyperthreading technology (e.g. Pentium 4)
are equivalent to two standard CPUs (e.g. 1 x Hyperthreaded CPU = 2 threads).
Address and Port defines the parameters for the TCP/IP connection:
the first one is the IP (e.g. XXX.XXX.XXX where XXX is a number in 0 to 255
range) or the nameserver entry (e.g. myserver.mydomain) of the remote host, and
the second one is the telnet service listening port that must be in the 1 to
65535 range (default 23). For security reasons, it's recommended to change the
default listening port from 23 to anyone different (e.g. 7000), because the
default port is the first one attacked by the hackers. This change must done in
the remote host telnet service and in the VEGA ZZ host configuration panel at
the same time: the two port numbers must be the same.
User name and Password are optional arguments: they are the
credentials to login to the remote host. In the Confirm field, you must
repeat the password in order to validate it.
Checking Encryption, it will be used the super-secure encrypted
connection and the encryption key (WarpKey) is required: it must be 64
characters long and it must contain hexadecimal digits only (e.g.
0123456789ABCDEF). The WarpKey must be the same used by the remote host
connection services (WarpGate or
WarpTel). Clients and hosts with
different keys can't communicate each other. If you need to create a new
encryption key, you could click the Gen. Key button or the external
utility called WarpKeyGen.
All host changes will be effective clicking Apply button. If you
change the host without clicking Apply, all changes will be lost. If a
wrong parameter is found, its field is highlighted and the error message is
shown in the bottom window bar.
The host list is saved clicking Save button and if you close the
window after a change without saving it, a warning message is shown.